一、配置 MyBatis(XML 形式) src/main/resources/mybatis-config.xml:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd" > <configuration > <properties resource ="jdbc.properties" > </properties > <settings > <setting name ="logImpl" value ="LOG4J" /> </settings > <typeAliases > <package name ="tk.mybatis.simple.model" /> </typeAliases > <environments default ="development" > <environment id ="development" > <transactionManager type ="JDBC" > <property name ="" value ="" /> </transactionManager > <dataSource type ="UNPOOLED" > <property name ="driver" value ="${jdbc.driver}" /> <property name ="url" value ="${jdbc.url}" /> <property name ="username" value ="${jdbc.username}" /> <property name ="password" value ="${jdbc.password}" /> </dataSource > </environment > </environments > <mappers > <mapper resource ="tk/mybatis/simple/mapper/CountryMapper.xml" /> </mappers > </configuration >
二、具体语句 1. Insert insert 返回主键
1.1. 只适用于支持主键自增的数据库 1 2 3 4 5 6 <insert id ="insert2" useGeneratedKeys ="true" keyProperty ="id" > insert into sys_user( user_name, user_password) values( #{userName}, #{userPassword}) </insert >
1.2. 使用 selectKey 返回主键的值 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 <insert id ="insert2" useGeneratedKeys ="true" keyProperty ="id" > insert into sys_user( user_name, user_password) values( #{userName}, #{userPassword}) <selectKey keyColumn ="id" resultType ="long" keyProperty ="id" order ="AFTER" > SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID() </selectKey > </insert >
Oracle:
1 2 3 <selectKey keyColumn ="id" result ="long" keyProperty ="id" order ="BEFORE" > SELECT SEQ_ID.nextval from dual </selectKey >
2. select 1 2 3 4 5 6 <select id ="selectAll" resultType ="tk.mybatis.simple.model.SysUser" > select id, user_name userName, user_password userPassword from sys_user </select >
使用 resultType 需要设置别名来实现自动映射
三、注解方式 1. @Select 注解 1.1. 通过别名自动映射 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @Select({"select id, role_name roleName ", "from sys_role ", "where id = #{id}"}) SysRole selectById (Long id) ; @Select({"select id, role_name roleName from sys_role where id = #{id}"}) SysRole selectById (Long id) ;
1.2. 使用 resultMap 方式 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 @Results(id = "roleResultMap", value = { @Result(property = "id", column = "id", id = true), @Result(property = "roleName", column = "role_name") }) @Results({ @Result(property = "id", column = "id", id = true), @Result(property = "roleName", column = "role_name") }) @Select("select id, role_name from sys_role where id = #{id}") SysRole selectById2 (Long id) ; @ResultMap("roleResultMap") @Select("select * from sys_role") List<SysRole> selectAll () ;
2.1. 返回自增主键 1 2 3 4 @Insert({"insert into sys_role(role_name)", "values(#{roleName})"}) @Options(useGeneratedKeys = true, keyProperty = "id") int insert2 (SysRole sysRole) ;
2.2. 返回非自增主键 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @Insert({"insert into sys_role(role_name)", "values(#{roleName})"}) @SelectKey(statement = "SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID()", keyProperty = "id", resultType = Long.class, before = false) int insert3 (SysRole sysRole) ;
3. Provider 注解 1 2 @SelectProvider(type = PrivilegeProvider.class, metod = "selectById") SysPrivilege selectById (Long id) ;
PrivilegeProvider:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public class PrivilegeProvider { public String selectById (final Long id) { result new SQL () { { SELECT("id, privilege_name, privilege_url" ); FROM("sys_privilege" ); WHERE("id = #{id}" ); } }.toString(); } }
四、动态 SQL 1. if 用法 1 2 3 <if test ="userName != null and userName != ''" > and user_name like concat('%', #{userName}, '%') </if >
2. choose 用法 1 2 3 4 5 6 <choose > <when test ="userName != null" > ... </when > <otherwhise > </otherwhise > </choose >
3. where set trim 用法 3.1. where 用法 1 2 3 4 5 <where > <if test ="userName != null and userName != ''" > and user_name like concat('%', #{userName}, '%') </if > </where >
3.2. set 用法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 <update id ="updateByIdSelective" > update sys_user <set > <if test ="userName != null and userName != ''" > user_name = #{userName}, </if > <if test ="userPassword != null and userPassword != ''" > user_password = #{userPassword}, </if > </set > where id = #{id} </update >
3.3. trim 用法 where 标签对应 trim 的实现:
1 2 3 <trim prefix ="WHERE" prefixOverrides ="AND |OR" > ... </trim >
set 标签对应的 trim 实现:
1 2 3 <trim prefix ="SET" suffixOverrides ="," > ... </trim >
prefix: 给内容增加 prefix 指定的前缀
prefixOverrides: 把内容中匹配的前缀字符串去掉
suffix: 给内容增加 suffix 指定的后缀
suffixOverrides: 把内容中匹配的后缀字符串去掉
4. foreach 用法 1 2 3 4 where id in <foreach collection ="list" open ="(" separator ="," close =")" item ="id" index ="i" > #{id} </foreach >
5. bind 用法 1 2 3 4 <if test ="userName != null and userName != ''" > <bind name ="userNameLike" value ="'%' + userName + '%'" /> and user_name like #{userNameLike} </if >
五、高级结果映射 1. 一对一映射 1.1. 使用自动映射 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <select id ="selectUserAndRoleById" resultType ="tk.mybatis.simple.model.SysUser" > select u.id, u.user_name as userName, u.user_password as userPassword, r.id as "role.id", r.role_name as "role.roleName" from sys_user u inner join sys_user_role ur on u.id = ur.user_id inner join sys_role r on ur.role_id = r.id where u.id = #{id} </select >
1.2. 使用 resultMap 配置一对一映射 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <resultMap id ="userRoleMap" type ="tk.mybatis.simple.model.SysUser" > <result property ="id" column ="id" /> <result property ="userName" column ="user_name" /> <result property ="userPassword" column ="user_password" /> <result property ="role.id" column ="role_id" /> <result property ="role.roleName" column ="role_name" /> </resultMap >
1.3. 使用 resultMap 的 association 标签配置一对一映射 1 2 3 4 5 6 <resultMap id ="userRoleMap" type ="tk.mybatis.simple.model.SysUser" > <association property ="role" columnPrefix ="role_" javaType ="tk.mybatis.simple.model.SysRole" > <result property ="id" column ="id" /> <result property ="roleName" column ="role_name" /> </association > </resultMap >
2. 一对多映射 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 <resultMap id ="userRoleListMap" extends ="userMap" type ="tk.mybatis.simple.model.SysUser" > <id property ="id" column ="id" /> <result property ="userName" column ="user_name" /> <result property ="userPassword" column ="user_password" /> <collection property ="roleList" columnPrefix ="role_" javaType ="tk.mybatis.simple.model.SysRole" > <id property ="id" column ="id" /> <result property ="roleName" column ="role_name" /> </collection > </resultMap >
3. 返回 Map 3.1. map 的 value 为 java 类 mapper.java
1 2 @MapKey("id") Map<Long, UserInfo> getUserInfoMap () ;
mapper.xml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <resultMap id ="UserResultMap" type ="com.xixicat.domain.UserInfo" > <result property ="id" column ="id" /> <result property ="username" column ="username" /> <result property ="sex" column ="sex" /> </resultMap > <select id ="getUserInfoMap" resultMap ="UserResultMap" > select id,username,sex from user_info </select >
3.2. map 的 value 为 map mapper.java
1 2 @MapKey("id") Map<Long, Map<String,Object>> getUserValueMap () ;
mapper.xml
1 2 3 4 <select id ="getUserValueMap" resultType ="map" > select id,username,sex from user_info from user_info </select >
3.3. 返回 List<Map<key, value>> mapper.java
1 List<Map<String, Object>> countInquireForMobile () ;
mapper.xml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 <select id ="countInquireForMobile" resultType ="map" > select o.status as `status`, count(mc.id) as `count` from mall_contract mc join mall_order o on o.contract_no = mc.contract_no where o.archive = false and o.flag = 0 and o.status in ('SUBMITTED', 'PAID', 'SHIPPED', 'SUCCESS') and o.refund_status = 'CREATE' <if test ="params.opUserType == 'BUYER'" > and o.buyer_id = #{params.operatorId,typeHandler=idHandler} </if > <if test ="params.opUserType == 'SELLER'" > and o.seller_id = #{params.operatorId,typeHandler=idHandler} </if > group by o.status </select >
4. 鉴别器映射 类似于 switch
1 2 3 4 5 6 <resultMap id ="rolePrivilegeListMapChoose" type ="tk.mybatis.simple.model.SysRole" > <discriminator column ="enabled" javaType ="int" > <case value ="1" resultMap ="rolePrivilegeListMapSelect" /> <case value ="0" resultMap ="roleMap" /> </discriminator > </resultMap >
5. 枚举处理器 在 mybatis-config.xml 中添加配置:使用枚举的索引进行处理
1 2 3 4 <typeHandlers > <typeHandler javaType ="tk.mybatis.simple.type.Enabled" handler ="org.apache.ibatis.type.EnumOrdinalTypeHandler" /> </typeHandlers >
6. 自定义处理器 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public class EnabledTypeHandler implements TypeHanlder <Enabled> { private final Map<Integer, Enabled> enabledMap = new HashMap <Integer, Enabled>(); public EnabledTypeHandler () { for (Enabled enabled : Enabled.values()) { enabledMap.put(enabled.getValue(), enabled); } } @Override public void setParameter (PreparedStatement ps, int i, Enabled parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException { ps.setInt(i, parameter.getValue()); } @Override public Enabled getResult (ResultSet rs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException { Integer value = rs.getInt(columnIndex); return enabledMap.get(value); } @Override public Enabled getResult (CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException { Integer value = cs.getInt(columnIndex); return enabledMap.get(value); } }
在 mybatis-config.xml 中配置:
1 2 3 4 <typeHandlers > <typeHandler javaType ="tk.mybatis.simple.type.Enabled" handler ="tk.mybatis.simple.type.EnabledTypeHandler" /> </typeHandlers >
六、缓存 1. 一级缓存 范围:
概述:
清空缓存:
flushCache=”true”:
1 2 3 <select id ="selectById" flushCache ="true" resultMap ="userMap" > select * from sys_user where id = #{id} </select >
2. 二级缓存 范围:
概述:
2.1. 在 mapper.xml 中配置 二级缓存全局开关: 不必配置,默认已为 true
1 2 3 4 <settings > <setting name ="cacheEnabled" value ="true" /> </settings >
开启二级缓存:
1 2 3 <mapper namespace ="tk.mybatis.simple.mapper.RoleMapper" > <cache /> </mapper >
默认的二级缓存会有如下效果
所有的 select 语句将会被缓存
所有的 insert、update、delete 语句将会刷新缓存
缓存会使用 LRU 算法来回收
根据时间表(刷新间隔),缓存不会以任何时间顺序刷新
缓存会存储集合或对象 1024 个引用
缓存会被视为 可读可写 的,所以返回的对象不是共享的,可以安全的修改
cache 可配置的属性:
1 <cache eviction ="FIFO" flushInterval ="60000" size ="512" readOnly ="true" />
eviction:收回策略
LRU(最近最少使用):移除最长时间不被使用的对象,默认
FIFO(先进先出):按对象进入缓存的顺序来移除它们
SOFT(软引用):移除基于垃圾回收器状态和弱引用规则的对象
WEAK(弱引用):更积极地移除基于垃圾收集器状态和弱引用规则的对象
flushInterval:刷新间隔。毫秒,默认不设置(没有刷新间隔,缓存仅在调用 sql 时刷新)。
size:引用数目。默认 1024
readOnly:只读。只读的缓存会给所有调用者返回缓存对象的相同实例,不能修改。默认 false
2.2. 在 Mapper 接口中配置二级缓存 当只使用注解方式配置二级缓存时:
1 2 3 4 @CacheNamespace public interface RoleMapper { ... }
配置属性:
1 2 3 4 5 6 @CacheNamespace( eviction = FifoCache.class, flushInterval = 60000, size = 512, readWrite = true )
当同时使用注解方式和 XML 映射文件时:
引用 Mapp 接口中配置的二级缓存
1 <cache-ref namespace ="tk.mybatis.simple.mapper.RoleMapper" />
2.3. 使用二级缓存 使用可读写缓存,通过序列化和反序列化来保证通过缓存获取数据时,得到的是一个 新的实例 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 sqlSession = getSqlSession(); try { RoleMapper roleMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(RoleMapper.class); SysRole role2 = roleMapper.selectById(1L ); Assert.assertEquals("New Name" , role2.getRoleName()); Assert.assertNotEquals(role1, role2); SysRole role3 = roleMapper.selectById(1L ); Assert.assertNotEquals(role2, role3); } finally { sqlSession.close(); }
2.4. 二级缓存适用场景
以查询为主的应用中,只有尽可能少的 curd
绝大多数以单表操作存在时,由于很少存在互相关联的情况,因此不会出现脏数据
分布式场景不能使用,需要借助第三方缓存中间件
2.5. 使用 redis 实现二级缓存
加入依赖
1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > org.mybatis.caches</groupId > <artifactId > mybatis-redis</artifactId > <version > 1.0.0-beta2</version > </dependency >
使用缓存
1 2 3 4 @CacheNamespace(implementation = RedisCache.class) public interface IUserMapper { ... }
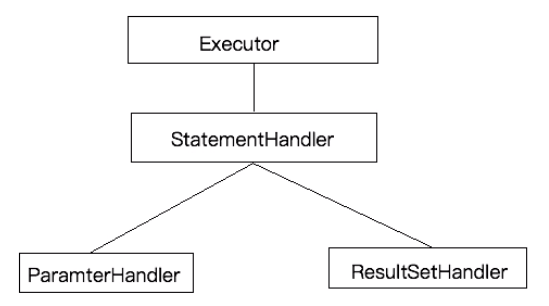
七、插件 1. 概述 对 mybatis 的扩展,其原理是拦截器,在四大组件(Executor、StatementHandler、ParamterHandler、ResultSetHandler)使用时拦截处理
允许拦截的方法:
Executor(执行器):update、query、commit、rollback
StatementHandler(SQL 语句构建器):prepare、parameterize、batch、update、query
ParameterHandler(参数处理器):getParameterObject、setParameters
ResultSetHandler(结果集处理器):handleResultSets、handleOutputParameters
原理:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public ParameterHandler newParameterHandler (MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object object, BoundSql sql, InterceptorChain interceptorChain) { ParameterHandler parameterHandler = mappedStatement.getLang().createParameterHandler(mappedStatement,object,sql); parameterHandler = (ParameterHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(parameterHandler); return parameterHandler; } public Object pluginAll (Object target) { for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) { target = interceptor.plugin(target); } return target; }
2. 自定义插件
实现 Interceptor 并添加注解
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 @Intercepts({ @Signature( // 指定组件 type = Executor.class, // 指定方法 method = "query", // 指定参数确定方法 args = {MapperStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class} ) }) public class ExamplePlugin implements Interceptor { @Override public Object intercept (Invocation invocation) throws Throwable { System.out.println("对方法进行了增强...." ); return invocation.proceed(); } @Override public Object plugin (Object target) { System.out.println("将要包装的目标对象" + target); return Plugin.wrap(target, this ); } @Override public void setProperties (Properties properties) { System.out.println("初始化参数" + properties); } }
配置到配置文件中
1 2 3 4 5 <plugins > <plugin interceptor ="com.xxx.plugin.ExamplePlugin" > <property name ="name" value ="Bob" /> </plugin > </plugins >